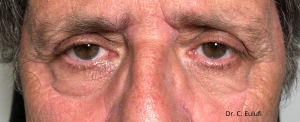
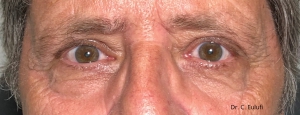
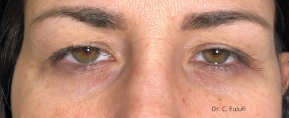
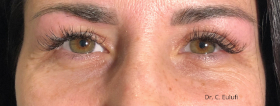
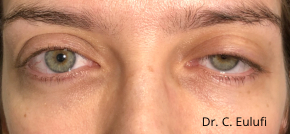
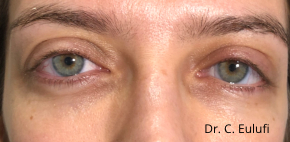
Clinical cases
Photos before and after by clicking here
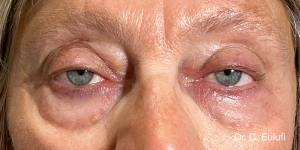
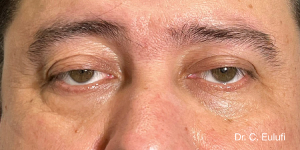
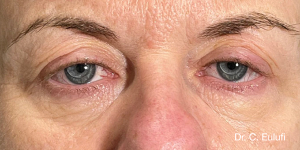
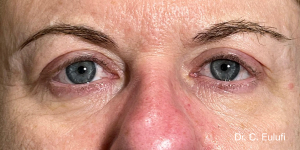
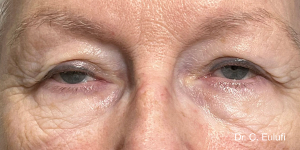
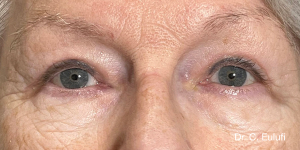
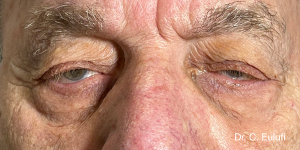
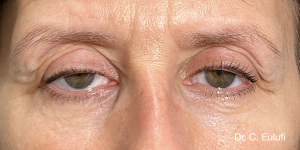
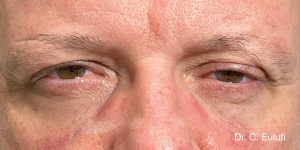
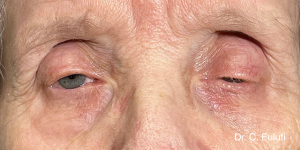
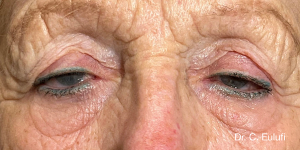
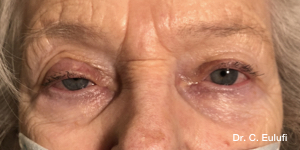
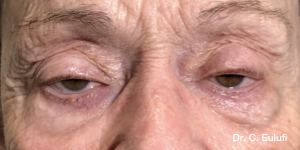
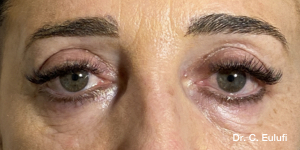
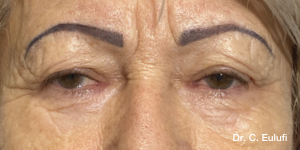
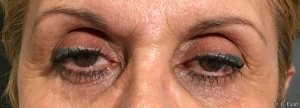
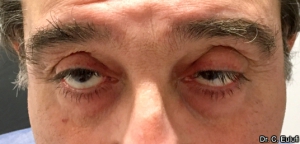
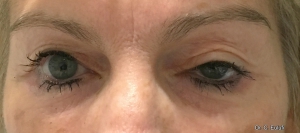
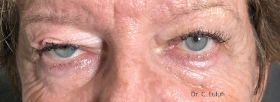
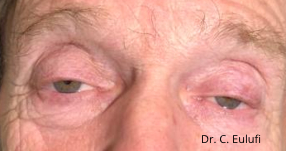
Ptosis palpebralis is the pathological drooping of the upper eyelid that usually occurs as a result of a dysfunction of the siphon muscle.
Several mechanisms may be responsible : neurogenic (caused by nerves), myogenic (caused by a deficit of the muscle), aponeurotic (usually due to age) or mechanical (e.g. after trauma) damage. However, ageing remains the main cause of ptosis.
Manifestations
The upper eyelid droops and partially or completely covers the eye, causing a restriction of the visual field.
The affected person has to tilt the head back or lift the eyelid with the finger to see, and uses the forehead muscles excessively.
Treatment
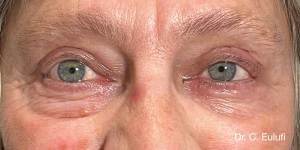
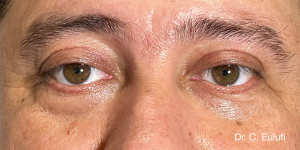
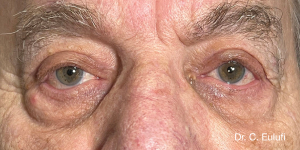
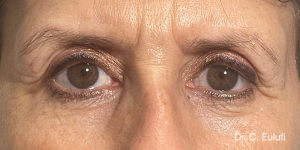
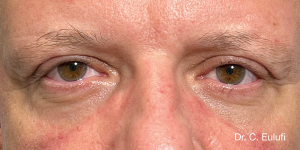
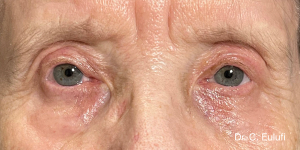
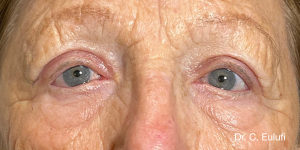
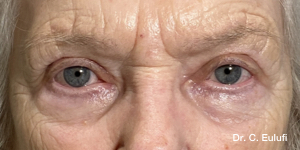
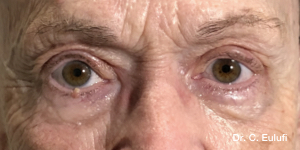
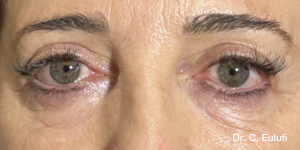
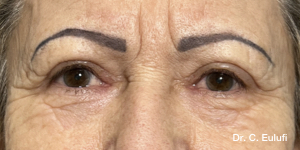
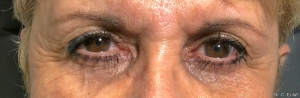
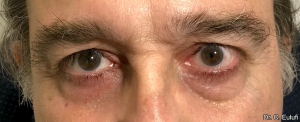
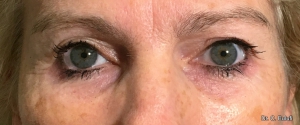
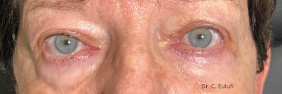
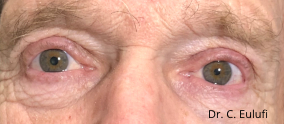
The outpatient surgical procedure is performed under local anaesthetic and involves repositioning the upper eyelid by lifting the eyelid, which restricts the field of vision.
There may be some degree of inflammation and bruising in the first few days after surgery, which usually subsides after 7 days.
We take care of all eye diseases,
from initial diagnosis to regular follow-up.